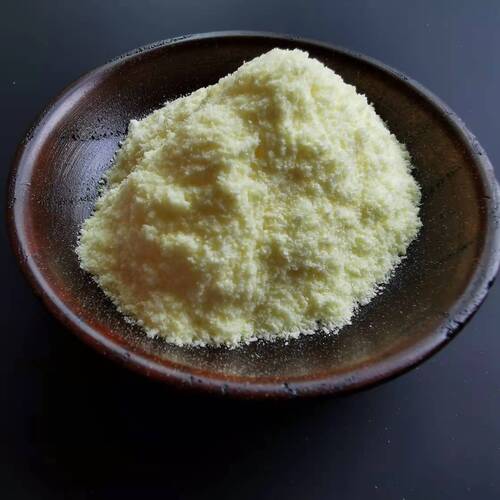
L-erythrothioneine USP cosmetics raw materials
Product Details:
L-erythrothioneine USP cosmetics raw materials Price And Quantity
- 1 Gram
- 1 USD ($)/Kilowatt
L-erythrothioneine USP cosmetics raw materials Trade Information
- Cash Against Delivery (CAD) Cash on Delivery (COD) Cash Advance (CA) Cheque
- Asia Australia Central America North America South America Eastern Europe Western Europe Middle East Africa
Product Description
Ergothioneine is a naturally occurring amino acid and is a thiourea derivative of histidine, containing a sulfur atom on the imidazole ring.[1] This compound occurs in relatively few organisms, notably actinomycetota, cyanobacteria, and certain fungi.[2][3] Ergothioneine was discovered in 1909 and named after the ergot fungus from which it was first purified,[4] with its structure being determined in 1911.[5]
In humans, ergothioneine is acquired exclusively through the diet and accumulates in erythrocytes, bone marrow, liver, kidney, seminal fluid, and eyes.[6] Although the effect of ergothioneine in vivo is under preliminary research, its physiological role in humans is unknown.[6] Ergothioneine is sold as a dietary supplement.[7]